The Highlands Highway is a critical 430 kilometer, two-lane national road that serves as the main transport artery for Papua New Guinea’s highland region. It connects approximately 1,800 kms of regional and feeder roads, providing essential access for communities in rural areas.
The Sustainable Highlands Highway Investment Program (SHHIP) is a 10-year joint initiative of the Government of Papua New Guinea (GoPNG) and the Asian Development Bank (ADB). The primary objective of SHHIP is to rehabilitate, restore, upgrade, and maintain the Highlands Highway stretching from the Lae Nadzab Airport junction in Morobe Province to Kagamuga airport junction near Mount Hagen in Western Highlands Province.
In addition, the SHHIP supports capacity development for the broader transport sector. The program uses the Highlands Highway as a pilot project for sustaina le road maintenance, promoting a holistic approach to sustainable maintenance. It promotes national cooperation and integration and widens access to social and economic opportunities via improved land transport infrastructue across Papua New Guinea.
Trench-1 of the SHHIP was divided into three separate sections, each involving various construction and rehabilitation works. The focus areas were on rehabilitating the road pavement structures, improving drainage elements, and improving side road slope stability.
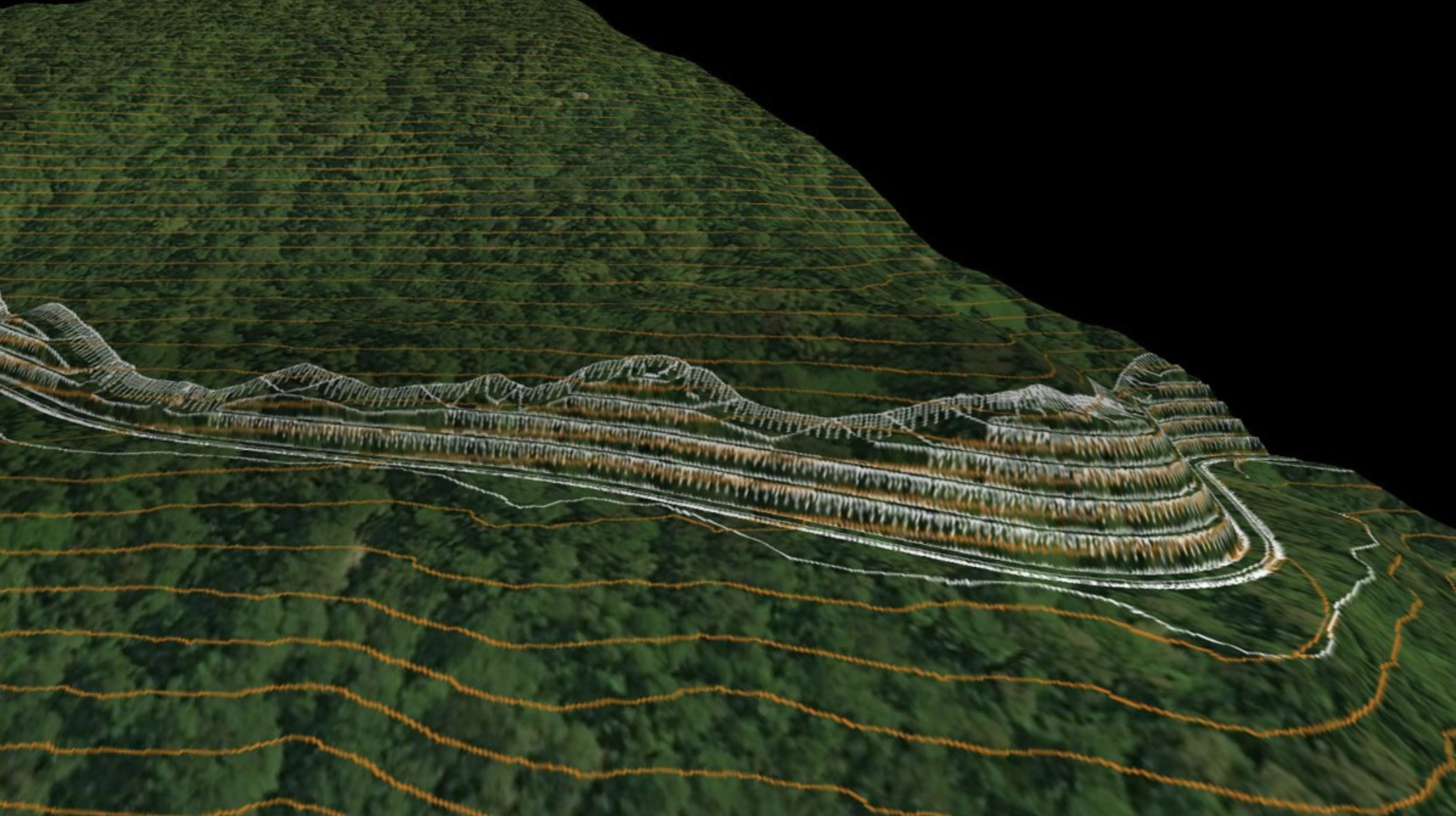
One of the sections, RIC, covers a 56-km stretch through Chimbu Province. This segment included 21 critical sites, which have been prone to landslides causing severe damages to the highway. At times, this caused complete closure of the highway to traffic, leading to severe social and economic consequences to the surrounding communities and road users who rely on the highway for access and transport.
To address these ongoing challenges, it was necessary to first conduct investigations to determine the cause of failure of each of the sites. Based on these findings, tailored approaches were developed to remedy the problem. A solution was required that would integrate design elements that enhance the climate resiliency of these sections of the highway.
In 2015, prior to the SHHIP agreements and project approval by the ADB, AnyWay conducted a thorough investigation of each of the critical sites. The investigation was conducted by a dedicated team of experts using advanced technologies for surveying, soil sampling and analysis, and physical site investigations and analysis. The team dedicated weeks of work on site, working rigorously to identify the root cause of failure for each of the sites. A comprehensive report was prepared and presented to the DOWH. This report formed the basis for initiating the detailed design phase for the critical sites under the SHHIP.
In 2019, building on the conclusions of the previous investigation, the detailed design work started. Designs were developed for each of the sites, taking into consideration the unique cause of failure and geological and geotechnical conditions at each location.
The detailed designs were tailored to account for the unique and specific conditions of each location. Climate resilient sustainable slope stability was achieved with practical yet innovative techniques and solutions to mitigate the reoccurring landslides.
We conducted thorough investigations of the cause of failure, including comprehensive materials sampling and testing, ran advanced slope stability models and prepared the design of all relevant elements to ensure resiliency and sustainability of each site under sever climatic events.
To achieve this, extensive investigations were carried out to understand the root causes of failure. This included comprehensive material sampling and testing, advanced slope stability modeling, and the design of all necessary structural and drainage components to ensure long-term performance under severe climatic conditions.
The adopted engineering approach focused on managing subsurface water on the upper slopes. Water was redirected through specially designed underground geotechnical elements into a robust drainage system. This system guided the water to predetermined crossing points beneath the road pavement and safely discharged it on the lower downhill slope. The design also included a reinforced pavement structure, with advanced ground stabilization measures incorporated into the lower slope adjacent to the road, ensuring long-term durability and stability.
Added value from AnyWay Solutions
AnyWay’s comprehensive approach to engineering design expanded the range of practical solutions available to the DOWH for addressing similar challenges in other roads and areas of the country.
Through these designs, AnyWay was able to not only able solve a long-time occurring problem but also introduced climate resilient transport infrastructure.The Highlands Highway is a vital economic and social lifeline for many communities in the region. Through these designs, AnyWay contributed to strengthening that lifeline, ensuring safer and more reliable connectivity for years to come.
This design approach directly contributes to achieving 9 of the 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), by fostering resilient infrastructure, promoting sustainable economic growth, and improving access to essential services in one of the country’s most important regions.